
Unreal Engine 5 for Enterprise Applications and Real-Time 3D Use Cases
Explore how Unreal Engine 5 for enterprise applications is used and how organizations are using it in the real world.
Continue Reading
Imagine wanting to review your expenses and manage your finances, so you open an app on your phone and instantly see a 3D model of your spending trends for the month, which is attractive, animated, and easy to understand.
No bank branch.
No wait time.
Just your finances, easy to understand at a glance.
Sounds futuristic?
Not anymore.
Augmented Reality (AR) is now not only about gaming or social media filters. It is also changing the game of the financial sector and transforming customer-bank interactions and customer money management.
At this point, many banks are leveraging AR to boost engagement, convenience, and trust. AR is being used for digital transformation in the finance sector through virtual branches, AR ATMs, interactive financial education tools, and more.
Let’s explore the key benefits of AR in banking, along with real-world use cases that demonstrate how it’s already changing the game.

The AR world market is growing very fast, and the banking industry is also starting to take advantage of it to improve its services.
Although many people are aware that AR is already being widely used in retail, healthcare, and in the gaming sector, nowadays, many don’t know that financial institutions also use the advantage of using it to create great customer experiences and to gain a competitive advantage.
According to recent reports, the AR BFSI market is expected to grow significantly over the next few years and is projected to be valued at $18.47 billion by 2034, and this growth is due to various reasons and some of which are:
Now, banks no longer only consider the possibility of adding AR, but they are already wondering when it can be added. You might not realize that the change takes place quickly, with the transition already being explored by major players with AR-based apps, digital assistants, and services that lack branches.
AR in banking is already being put into action in creative, customer-first ways.
Be it improving mobile banking applications or redesigning financial education, AR is assisting banks to be unique as well as simplifying monetary issues for all people.
Let’s have a look at 11 powerful use cases showing how AR is reshaping the banking experience:
AR tools are proving to be highly effective in helping users better understand their financial habits, budgets, and investment options. Customers can take the help of AR in financial services and simply scan their expenses, and can also see their spending segmented into real-time categories. This also helps in simplifying investment decisions for the customers by providing interactive insights on stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
Example:
Desjardins Bank’s AR-powered platform “Your Way Desjardins” features a virtual assistant named Penny. Using storytelling and videos, Penny offers personalized investment advice and financial education, making complex information easy to understand for every user.
Filing insurance claims, especially after accidents or property damage, can be time-consuming, right? You don’t need to worry now, as AR now allows policyholders to capture images or videos of damaged assets and submit them via mobile, helping with communication and speeding up approvals.
Example:
An example of AR in insurance is Allianz, which has developed an AR-based insurance app that lets users visually document property damage. This reduces paperwork and improves claim accuracy by adding repair cost estimates and contractor details within the same platform.
Another example of AR baking is how now banks and financial institutions are using AR to provide immersive previews of their offerings. Doesn’t matter if it’s a credit card, mortgage, or reward plan because customers can now explore features and benefits through engaging AR portals.
Example:
AR app developed by Mastercard provides the user with a 360-degree virtual experience so the customer can get a visual experience of their products. This not only increases interest but also allows the customers to make better decisions with more confidence.
We all know how hard it is to manage investment portfolios because it’s one of the things where you can’t afford to make mistakes, and due to this, it can be very overwhelming. AR can bring clarity by converting data into visually intuitive formats, making it easier for users to compare assets, spot risk factors, and adjust their strategies.
Example:
Fidelity Investments introduced StockCity, software that can turn a portfolio into an animated city, and all the facets thereof, including building height, traffic patterns, etc, could be used to describe financial indicators, with complicated figures and figures being depicted as a visual story.
One of the core strengths of AR in finance lies in its ability to simplify data interpretation. Users no longer have to go through a spreadsheet to analyze key metrics since they can use immersive dashboards and 3D charts.
Example:
Westpac Banking Corporation in Australia leverages smartphone-based AR for financial data visualization. By scanning their credit or debit cards, users can view their balance, transactions, and spending behavior in the form of 3D bar charts.
With the growth of contactless experiences, AR is being used to facilitate more intuitive payment systems. Customers can now complete transactions by simply pointing their phones at a product, no need for typing or tapping.
Example:
Visa Europe partnered with Blippar to develop an AR app that allows consumers to pay by scanning products. This not only speeds up the process but adds a futuristic edge to everyday shopping.
With cyber threats on the rise, digital banking security has never been more critical. In 2023 alone, a staggering 72.7% of all organizations experienced a ransomware attack, highlighting the urgent need for more robust protection. Augmented reality is now playing a vital role in enhancing financial security by integrating with biometric technologies such as facial recognition, iris scanning, and voice authentication.
Example:
USAA, a U.S.-based institution known for its innovation in mobile banking, has implemented biometric features such as facial and voice recognition within its app, requiring a blink to verify identity and a spoken phrase for voice confirmation. These features are layered into a multi-factor authentication framework that complements PINs and security tokens, offering enhanced protection with minimal friction
Augmented trading platforms are changing how investors interact with financial markets. AR allows users to visualize trading strategies, monitor market changes in 3D, and access holographic workstations, enhancing both strategy and speed.
Example:
Citigroup has integrated AR with Microsoft HoloLens to offer clients holographic trading stations. Investors can interact with live market data in real-time, improving decision-making across the board.
Banks are also using AR and VR for internal training by replicating real-world scenarios. This helps staff improve their service delivery, understand customer behavior, and respond effectively to various situations.
Example:
TD Bank Group teamed up with Remio to create VR simulations for their staff. These virtual environments helped employees role-play different customer service scenarios and boost workplace performance.
AR enhances physical banking support by providing detailed real-time information about nearby branches or ATMs. It can also guide users through banking tasks while ensuring data is integrated securely for convenience.
Example:
PrivatBank in Ukraine uses AR to give customers real-time assistance with locating services, accessing accounts, and even conducting transactions. With AR, tasks like authentication and security become more intuitive and efficient.
Locating the nearest ATM or bank branch is now faster and more intuitive with the help of augmented reality. Instead of typing in addresses or navigating static maps, customers can simply point their smartphones in any direction and instantly see nearby ATMs or branches overlaid onto their real-world surroundings. This real-time, location-based experience not only saves time but also minimizes frustration, especially when users are in unfamiliar areas or need quick access to services.
Example:
The Bank of Oman has embraced this innovation with its “NBO AR” mobile app. This cutting-edge tool uses AR technology to guide customers to the nearest NBO branches and ATMs through a real-world overlay on their smartphone screens, marking a significant step in the bank’s digital transformation journey and commitment to improving customer convenience.
By blending physical and digital experiences, banks can offer more transparency, convenience, and engagement to their customers.
As AR tech becomes more accessible, expect to see even more banks tapping into its potential to build smarter, friendlier financial experiences.

AR is no longer reserved for gaming or entertainment; it’s proving to be a powerful tool in reshaping the banking experience.
As customer expectations evolve and digital convenience becomes a norm, AR helps banks stay relevant by offering immersive, personalized, and highly intuitive services.
Here are some key benefits that banks and their customers are already starting to enjoy:
Traditional banking apps can often feel transactional and dull. AR adds an interactive layer that keeps users more engaged with their finances.
For example, instead of just viewing your balance, you can explore it in the form of animated graphs, 3D spending maps, or visual savings goals. These engaging formats hold the user’s attention longer and make routine banking tasks more satisfying.
This type of engagement builds stronger emotional connections between the customer and the bank, turning the app into a helpful financial companion rather than just a tool.
Financial data can be dense, overwhelming, and hard to digest on flat screens, especially for non-experts. AR changes that translate complex numbers into visual experiences.
Users can view spending patterns, loan options, investment forecasts, and credit reports as interactive charts, floating bars, or simulations. This reduces cognitive load and helps users better understand their financial situation at a glance.
For businesses and analysts, AR also supports collaborative decision-making through shared virtual dashboards that teams can interact with together.
One of the standout benefits of AR is that it brings banking services to the user, anytime, anywhere. Virtual bank branches, interactive onboarding, and real-time service guidance mean customers no longer need to physically visit a branch for most tasks.
Whether you’re in your home office or on the go, AR-powered tools allow access to support, transactions, and financial products in a highly visual and personalized format, removing location and time barriers.
This is especially impactful in rural areas or developing countries where physical infrastructure may be limited, but smartphone penetration is high.
Another AR in banking use case is personalized financial guidance. AR opens the door to highly personalized, data-driven experiences. Imagine opening your banking app and being greeted by a virtual assistant who knows your goals, habits, and financial history, and tailors suggestions accordingly.
This could include showing you a visual breakdown of your current expenses, alerting you about subscription renewals, or recommending smarter budgeting strategies, all through real-time, interactive overlays.
It replaces cold, generic dashboards with warm, intuitive, and contextual advice that speaks directly to the user.
Opening a new bank account or applying for a product like a credit card or mortgage usually involves multiple steps, which can frustrate users, especially first-timers.
AR streamlines this by guiding users step-by-step through the process with on-screen prompts, animations, and real-time support. Instead of reading long FAQs or calling customer service, users are shown exactly what to do and where to tap or scan.
This reduces drop-offs, enhances user satisfaction, and ensures fewer errors in form submissions.
In a saturated market where most banks offer similar services, AR can serve as a strong differentiator. Banks that adopt AR early position themselves as forward-thinking, customer-centric, and tech-savvy.
This is especially attractive to younger, digital-native customers who are more likely to choose financial services that offer innovation and convenience.
Moreover, AR features can give banks a fresh marketing edge, making their products more shareable, memorable, and exciting to explore.
Traditional financial literacy programs often fail to engage. AR solves this by turning financial education into an immersive and even entertaining experience.
Users can learn how loans work by adjusting sliders on 3D models, understand credit scores through interactive visuals, or explore compound interest via animated simulations.
This is particularly effective for young adults, students, and first-time savers, helping them build foundational money skills in a format they enjoy using.
Financial decisions often come down to understanding trade-offs, but traditional tools rarely make these trade-offs easy to see. AR helps users make better choices by visualizing the outcome of each option.
Want to know how a 20-year mortgage compares to a 30-year one? Or what will your budget look like after buying a new car? AR can simulate those outcomes, helping users “see” before they decide.
This gives customers greater confidence, reduces decision fatigue, and builds trust in the bank’s tools.
AR banking is more than just a visual upgrade; it’s a strategic leap toward smarter, more human-centered finance.
By making banking more intuitive, accessible, and engaging, AR not only enhances the user experience but also helps banks increase loyalty, drive adoption, and lead in a highly competitive landscape.
As the technology becomes more mainstream, banks that invest in AR now will be far ahead in creating the future of digital finance.
Contact us to build and enhance banking experiences with Augmented Reality.
Get StartedAs exciting and promising as AR in finance sounds, the road to full-scale adoption isn’t without bumps.
Many banks are eager to innovate, but implementing AR technology comes with its own set of challenges, from high costs to user readiness and everything in between.
Let’s explore the most common hurdles banks face and why solving them requires more than just tech investment.
Creating an AR experience isn’t cheap. It requires advanced software, skilled developers, and often third-party AR platforms, none of which come at a small price.
And it’s not just about building an app feature. Banks must integrate AR into their existing digital ecosystem while ensuring that it works seamlessly with legacy systems like core banking software, CRM tools, and data warehouses.
Example:
A mid-sized bank may want to launch an AR feature for visualizing financial goals, but the upfront development cost and backend integration might outweigh short-term ROI, especially without guaranteed user adoption.
Banking is all about trust. And when you add AR, which uses real-time cameras, location data, and sometimes facial recognition, the risk of privacy breaches increases.
Customers may hesitate to use AR features that require access to their camera or personal space, fearing surveillance, data leaks, or misuse of sensitive financial information.
Example:
An AR branch locator might ask for camera and GPS access. If users aren’t reassured about how their data will be used or protected, they’re likely to deny access or uninstall the feature altogether.
Not all users have access to AR-ready devices. For AR features to work smoothly, customers need modern smartphones with decent processors, sensors, and camera quality.
This immediately limits the reach of AR to tech-savvy or higher-income segments, leaving out a large chunk of the population who still use mid- to low-range devices.
Example:
A cutting-edge AR investment simulator might look great on a new iPhone, but on older Android devices, it may lag, crash, or not function at all, leading to frustration instead of engagement.
Let’s be honest: not every customer wants (or knows how) to use AR.
For many users, traditional mobile banking already does the job. Introducing AR features without clear value can confuse or overwhelm users, especially older demographics or non-tech-savvy customers.
Example:
A bank might roll out a feature that allows users to “scan” their card to see expense graphs in 3D. But if users don’t understand how it helps them more than regular charts, they may never try it, or worse, abandon the app.
Banking is one of the most heavily regulated industries. Introducing AR means capturing new types of data, offering virtual services, and potentially using biometric or geolocation-based information, all of which raise red flags for compliance teams.
Banks need to ensure that AR features don’t violate data protection laws like GDPR or local financial regulations.
Example:
If an AR onboarding tool scans a user’s face or ID for verification, it must meet strict legal requirements around biometric data storage and usage, which may differ by region and slow down rollout.
AR isn’t a “build it and forget it” technology. It requires regular updates to keep up with new devices, operating system changes, and evolving user expectations.
This ongoing maintenance can be resource-heavy, especially for banks without large in-house tech teams.
Example:
An AR-powered financial advisor might work flawlessly today, but after an iOS update, visual glitches or crashes could appear, affecting the user experience and brand perception unless addressed immediately.
While AR looks impressive, banks still struggle to quantify its return on investment. Does it increase customer retention? Does it drive revenue? Without clear metrics or use cases showing measurable success, stakeholders may hesitate to greenlight large-scale AR projects.
Example:
An innovation team might pitch an AR mortgage calculator, but executives could push back, asking whether it will actually bring in more loan applications or just serve as a nice gimmick.
The future of AR in financial services is bright, but not without its challenges.
To fully unlock its potential, banks need to look beyond the “wow” factor and focus on solving real user problems. That means investing in security, simplifying the experience, educating customers, and ensuring AR delivers clear, measurable value.
Because at the end of the day, even the flashiest tech won’t matter if it doesn’t make banking easier, safer, and more meaningful for the customer.
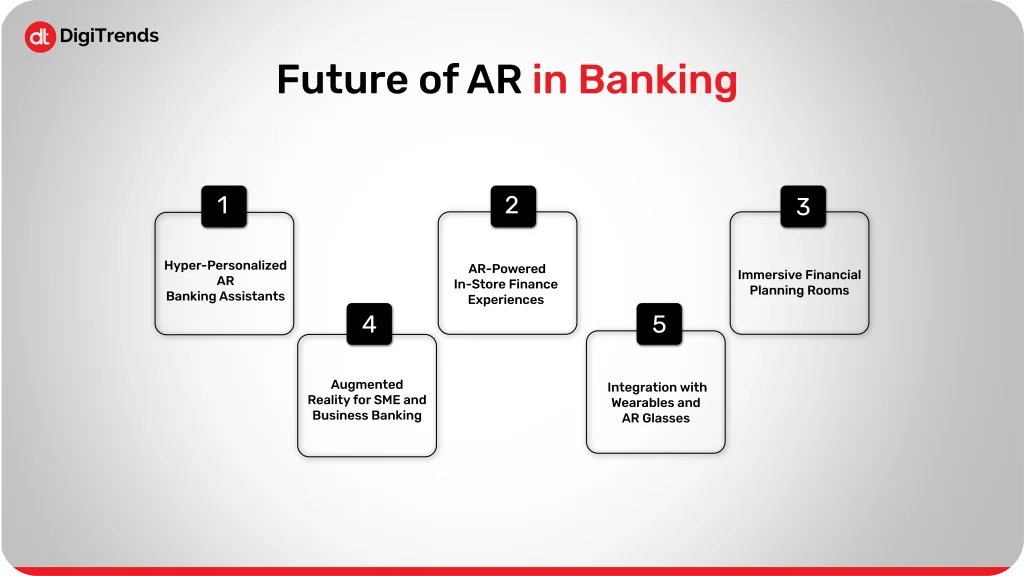
AR in financial services is still in its early chapters, but what’s ahead looks even more exciting.
With rapid advancements in tech, shifting customer expectations, and the rise of digital-first lifestyles, banks are exploring ways to take AR beyond visual gimmicks and turn it into a core part of the banking experience.
Here are some of the biggest AR trends that are likely to shape the future of finance:
Imagine opening your banking app and being greeted by a 3D virtual assistant who knows your name, financial goals, and recent activity.
In the future, banks will use AR to power hyper-personalized virtual assistants that offer smart advice in real time, whether it’s budgeting tips, investment suggestions, or reminders to pay your bills.
These assistants won’t just answer questions, they’ll visually guide users, show projections, and even help them compare financial products side by side.
Example:
Think of it as Siri or Alexa, but instead of just talking, it appears in front of you with visual aids that make money matters easier to grasp.
Retailers and banks are set to collaborate more closely, bringing banking right into the shopping experience.
Soon, customers could use AR in stores to scan price tags and instantly see financing options, cashback offers, or payment plans provided by partner banks.
Example:
While buying a new TV, a user could scan it with their phone and instantly view a pop-up comparing installment options from different banks, all without speaking to a salesperson or opening multiple apps.
Instead of reviewing budgets on spreadsheets, users may soon walk into virtual “finance rooms” where they can interact with different aspects of their money in 3D.
These spaces could feature floating graphs, trendlines, avatars for different goals (like saving for college or retirement), and simulation tools that respond to your actions in real time.
Example:
A family could sit together, put on augmented reality glasses, and visualize their joint financial goals, watching how monthly decisions impact their savings over time.
So far, most AR use cases have focused on individual customers, but small businesses are next.
Banks will begin offering AR dashboards that help entrepreneurs visualize cash flow, inventory levels, invoice statuses, and loan eligibility in real time.
This could be a game-changer for business owners who want financial clarity but don’t have time to dig through spreadsheets.
Example:
A shop owner could point their phone at their storefront and instantly see sales trends, incoming payments, and inventory alerts as visual overlays on the real world.
As devices like Apple Vision Pro and other smart glasses become mainstream, banks will start building AR experiences tailored for hands-free access.
This could include viewing notifications, checking balances, or even navigating a virtual bank branch without needing to pick up a phone.
Example:
A user wearing AR glasses could look at their credit card and instantly see a floating summary of their current balance, spending categories, and due date just by glancing.
The future of AR in banking isn’t just about better visuals; it’s about deeper connection, personalization, and convenience.
As the technology matures and becomes more affordable, we’ll see banks move from experimental features to full-scale augmented reality ecosystems, reshaping how we understand, manage, and interact with our money.
In a few years, opening your phone might feel less like banking and more like stepping into your own personal finance command center.
From helping users visualize their spending to turning financial education into an immersive experience, Augmented reality is no longer a “nice-to-have” in banking; it’s quickly becoming a strategic advantage.
Yes, the road to implementation comes with its share of challenges. But the potential? It’s massive.
As customer expectations shift toward hyper-personalized, intuitive, and tech-driven experiences, banks that invest in AR today are setting the stage for long-term loyalty and differentiation.
At DigiTrends, we understand that innovation isn’t just about adopting the latest tech; it’s about solving real problems in smarter ways.
That’s why we’re helping forward-thinking financial institutions bring AR to life through seamless strategy, scalable development, and human-centered design. Whether you’re exploring your first AR feature or planning an immersive financial platform, DigiTrends is your partner in building the future of digital banking.
Because the future of finance isn’t flat; it’s interactive.
And it’s already here.
