
Voice Recognition Technology in Healthcare: Benefits for Patients and Providers
Explore how voice recognition technology is being used across healthcare and the role of voice assistants in clinical environments.
Continue Reading
Imagine a surgeon performing a complex surgery while they can communicate with experts with digital overlays guiding each movement, or a medical student exploring the human body in 3D without picking up any tools.
This is the promise of (AR) augmented reality in healthcare.
AR delivers a mix of the real and the digital, changing how we diagnose, train, and treat. AR is no longer science fiction: it is already finding its purpose in hospitals and medical training, providing real-time information, an improved sense of visualization, and a hands-on learning experience like never before. With the increased adoption of technology in the medical field, AR is proving to be one of the most versatile technologies, transforming the field of modern medicine, with its reach projected to grow approximately 3.5 times by 2027.
Augmented Reality is becoming one of the most popular and highly impactful technologies for the healthcare industry. Augmented reality for healthcare is consistently listed among the top technology trends.
AR technology is helping merge digital visuals with physical environments. Whether it is training medical students or assisting doctors during complicated surgeries, AR is indeed opening new opportunities and solutions to all phases of healthcare delivery and education.
Let’s look at the key areas where AR is creating an impact in healthcare:
Medical students are usually taught about the human body through 2D diagrams; their understanding is hence limited, whereas AR offers an immersive learning experience. In AR, medical students are presented with 3D representations of organs, bones, and systems with anatomy correctness overlaid or through an AR headset. These models are rotatable, cut up virtually, and can be examined in many ways.
If medical students use AR in their learning and practice, they can ditch the old traditional methods. AR can help medical students to practice their skills, like injections or any other surgical steps, through simulation. Simulations can replicate in-life experiences, such as seeing a trauma patient or finding the symptoms, and can supplement important thinking skills and judgment in stressful moments. AR in medical training can not only help students understand better, but it also prevents putting real patients’ lives at risk during training.
Accuracy is everything in surgical care, and AR can serve to be a detailed surgical planning and training tool before important surgeries. Putting the data of MRI, CT, or sonography into an AR system, surgeons will be able to make models of organs, bones, tumors, and blood vessels of particular patients in 3D. These models can help surgeons prepare for their surgery before it starts and know about any complications that they can encounter during the surgery; this way, they will be well prepared for any obstacles during the surgery and can plan better.
During operation, these images can be projected as 3D on the body of the patient using AR displays or glasses. As an example, AR can be used during an orthopedic surgery to show precisely where an incision should be made, to place an implant, or to ensure that bones are aligned to within a sub-millimeter. The AR can guide through the brain structure, which is quite complex, without touching on some critical body areas during neurosurgery. Real-time visualization leads to higher levels of accuracy, reduced operation times, decreased errors, and eventually to faster patient recovery.
The doctors must explain everything in detail to their patients, and patients have a deep understanding of their condition because medical conditions can be hard to understand. Doctors usually explain the diagnosis to the patients through 2D images or just hand gestures. AR in patient education can help turn these 2D images into interactive visuals. For example, let’s say a patient is diagnosed with appendicitis and needs to be treated urgently, but they have zero knowledge about what this is and are scared of the surgery, doctors can use AR in this case to project a 3D image of the appendix in the patient’s body and show them how they’ll fix it. This can help increase patient satisfaction and trust.
Such clarity is beneficial not only in letting the patients know their diagnosis but also their treatment process. AR has helped increase biopsy success by 50% through accurate body scanning. Doctors just need smartphones and direct them to specific areas of the patient’s body to virtually map the body. AR-powered apps can also help patients acquire knowledge about their diagnosis and condition, their bodies, and the way drugs interact with them, and keep track of their treatment process.
AR is bringing a whole new experience of motivation and personalization of physical therapy by turning normal exercises into an interactive experience. With the help of AR applications, patients will be able to move around and get guided visually with the instructions superimposed on their actual reality, commonly as a game or a goal-oriented challenge.
These AR systems can track the patient’s motion and posture and provide them with instant feedback on their accuracy and progress. For example, someone recovering from a knee replacement can use an AR app that encourages specific exercises, shows how well they are performing, and adjusts the difficulty as they improve. This real-time suggestion not only motivates patients for therapy but also allows therapists to be remotely informed of progress and equipped to issue corrections without on-site visits. AR can help enhance the results and also take off some load from healthcare providers.
Access to specialized care is a significant challenge in rural or underserved areas. AR is helping close this gap by allowing healthcare professionals to collaborate remotely in real time through telemedicine apps. Through AR headsets like Microsoft HoloLens or AR-compatible tablets, local practitioners can share their field of view with distant specialists. These experts can then annotate the shared visual, highlight specific areas, or give step-by-step instructions that appear in the practitioner’s visual field.
In emergency surgery or trauma situations, where minutes matter, this kind of live remote assistance can be life-saving. It’s also proving valuable in educational settings, where a senior surgeon can guide multiple trainees remotely, explaining procedures while visual aids appear directly on their screens or headsets. In diagnostics, AR allows for real-time, guided ultrasound exams where a technician receives live visual support from a radiologist halfway across the world. This seamless integration of visual and verbal communication improves accuracy, saves time, and extends expert-level care to those who might otherwise go without.
The influence of augmented reality in healthcare is deeply impactful for the healthcare industry. By improving visualization, enhancing decision-making, and bringing more interactivity to patient care, it’s setting a new standard for innovation in medicine.

Although AR offers impactful advancements for the healthcare industry, it also comes with some challenges. From technical limitations to ethical concerns, the path to widespread adoption involves navigating several hurdles. Understanding these obstacles is essential to developing responsible, effective, and scalable AR solutions in healthcare.
AR devices such as headsets and smart glasses are quite expensive, which limits their reach on a large scale. Augmented Reality devices require developing AR applications and software, which further increases the costs. Small healthcare providers can find it difficult and out of budget to pair augmented reality and healthcare.
Creating a healthcare application requires security compliance according to the regulatory rules of GDPR and HIPAA, or other according to different regions. Just like that, AR apps and devices need to comply with the security regulations set by the FDA.
Pairing AR and healthcare comes with the risk of data breaches and privacy violations. To reduce this, secure data management systems are created to ensure that the platform complies with data protection regulations.
AR devices and systems are not easy to use; one needs to learn how to use them before using them to reduce any risks. For example, doctors who are not handy with using AR may end up putting the life of the patient at risk.
There are several challenges faced by healthcare providers when looking to integrate AR in their medical services, for example, a hospital with an active medical app looking to add AR to their app, and also add AR for their doctors to help them with critical surgeries. In this case, choosing the right development partner is the most important aspect to dodge all the challenges that come with pairing augmented reality and healthcare.
Organizations like DigiTrends have proven their expertise in providing digital solutions for the healthcare industry. Partnering with companies like DigiTrends will help you transform your healthcare operations with AR effectively.
As Augmented Reality continues to reshape healthcare, it’s equally important to tackle the barriers that hinder its widespread adoption. Addressing these challenges requires a combination of technical solutions, regulatory alignment, and stakeholder engagement.
Here are some strategic ways the industry can move forward:
Hospitals or healthcare providers who are looking to add AR in their medical procedures should train the doctors and nurses to use AR applications and devices so they don’t risk the patient’s life by messing up during medical procedures.
Handling sensitive patient information through AR requires strong data protection. End-to-end encryption should be standard in all AR solutions to secure data transfer and storage.
It’s also important to ensure compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA or GDPR. AR devices should come with built-in security features, and regular security audits can help identify any weak points.
High development and implementation costs can deter healthcare providers. One solution is to roll out AR solutions gradually, starting with specific departments like surgery or radiology.
Hospitals can also apply for government grants that support digital health innovation. In some cases, shared investment models between hospitals can reduce individual expenses while still enabling access to AR tools.
These strategies can help healthcare organizations overcome key barriers and fully embrace the potential of AR. With the right planning, training, and support, AR can become a valuable part of everyday clinical practice.
As technology continues to evolve, Augmented Reality is set to play an even greater role in transforming healthcare. The future holds several exciting possibilities, many of which are already in early stages of development or testing.
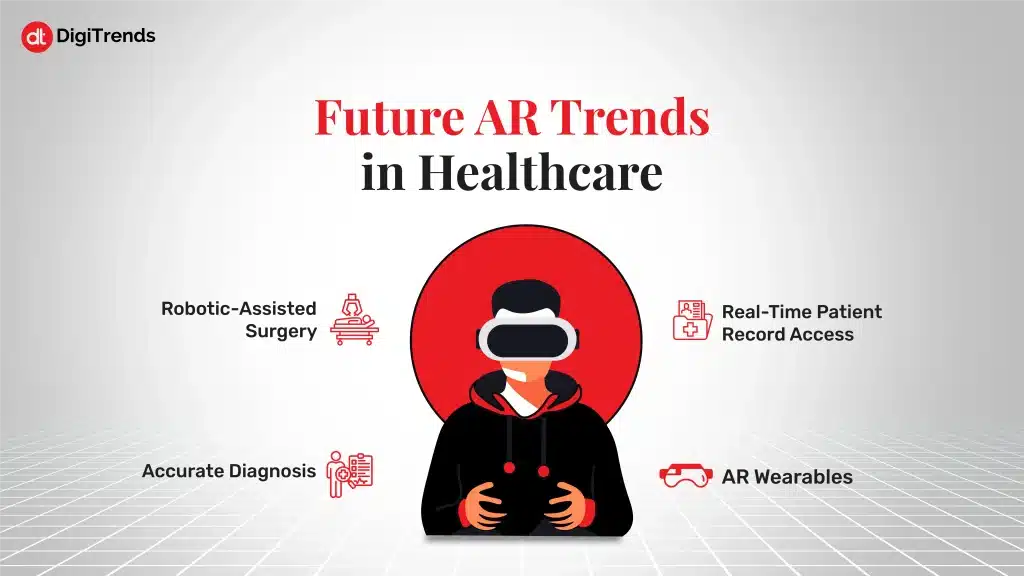
Let’s have a look at some of the trends expected to shape the future of augmented reality in medicine:
Surgeons can use AR overlays during robotic-assisted procedures to view internal structures in real time, improving accuracy and reducing the risk of complications. This combination allows for minimally invasive surgeries with quicker recovery times and better outcomes.
Shortly, AR may offer instant access to patient records right at the point of care. Doctors wearing AR glasses could view medical histories, lab results, and imaging data while interacting with the patient, all hands-free. This reduces time spent switching between devices and improves decision-making speed and efficiency.
AR tools will enhance diagnostic accuracy by providing real-time visualizations of scans and test results. For instance, doctors could project 3D images of organs, tumors, or fractures directly onto a patient’s body, making it easier to explain conditions and plan treatments. This level of visual clarity can lead to earlier detection and better patient understanding.
Next-generation AR wearables are expected to become more compact, affordable, and powerful. These devices will assist healthcare professionals during procedures, provide remote guidance, or even help patients manage chronic conditions. Wearables may also become essential tools in home healthcare, enabling real-time monitoring and support.
As these trends evolve, augmented reality in healthcare will redefine how medical services are delivered, from surgery to diagnosis to everyday clinical workflows. The future is not just digital, it’s immersive.
Augmented Reality is steadily transforming the landscape of modern healthcare. It is revolutionizing how medical professionals learn, make decisions, and perform complex procedures. Whether it’s through immersive training simulations, enhanced surgical planning, or real-time guidance during operations, AR is improving precision and efficiency across the board. It also enhances patient engagement by offering clear, visual explanations of conditions and treatments, helping build stronger trust between doctors and patients.
Despite the exciting potential, the road to adding augmented reality in healthcare isn’t without its hurdles. High development costs, data privacy concerns, and technical integration remain significant challenges. However, with strategic investments in training, security, and interoperability, these issues are increasingly being addressed. As healthcare systems and tech providers continue to collaborate, AR will likely shift from an emerging innovation to an everyday tool, reshaping care delivery, improving outcomes, and making healthcare more accessible, personalized, and effective.
If you are looking to integrate augmented reality in healthcare, organizations like DigiTrends offer end-to-end development services, from initial concept to final deployment. Whether you are looking to add AR to an existing telemedicine app or want to start from scratch, DigiTrends will help turn your vision into a successful solution for augmented reality in medicine.
